An Irish Republican Army (IRA) unit attacks Brookeborough Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC) barracks on January 1, 1957, in one of the most famous incidents of the IRA’s Operation Harvest (Border campaign). Two IRA men are killed as they attack Brookeborough police station in County Fermanagh. The attack is a military disaster for the IRA, but it proves a major propaganda coup.
The two dead men, Seán South and Fergal O’Hanlon, are hailed as republican martyrs. Their funerals are attended by thousands of people and their lives immortalised in republican ballads.
The Brookeborough raid is the central action in the IRA’s border campaign of 1956-62, yet it is over and done within a matter of minutes. The aim is to unite Ireland by setting up “liberated zones” in Northern Ireland and overthrowing the Stormont government. The campaign is preceded by a series of raids carried out by republican splinter group Saor Uladh. An attack on Rosslea police station in County Fermanagh in November 1955 results in the death of Saor Uladh member Connie Green.
Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC) officer Gordon Knowles finds himself on the sharp end of the assault as the republicans blow the front wall from the barracks. “I was blown right across the guard room,” he says. “The only thing I felt was like somebody hitting me in the back and that was the bullet going in through the left-hand side of the spine, round the back of the spine and lodging one inch from the back. They shone a torch in my face and said: ‘Oh, let’s go, he’s had it.'”
Knowles is lucky to be alive as medical staff discover thirteen bullet holes in his body. He recovers to resume his police career and still carries bullet splinters in his body to this day.
The Brookeborough raid, involving fourteen IRA men, is planned along identical lines to the Rosslea attack, with very different results. The IRA aims to explode a bomb in front of the police station and to seize RUC weapons.
Just two days previously, the police suffer their first death of the border campaign when Constable John Scally is killed in an attack on Derrylin barracks, another County Fermanagh border station.
Ahead of the Brookeborough attack, the men gather at the County Monaghan family home of Fergal O’Hanlon, who takes part in the raid. O’Hanlon’s sister Pádraigín Uí Mhurchadha describes the scene. “I remember Fergal, on the night, saying to my mother ‘These men, give them a good meal because there are faces here tonight you won’t see again.’ Now it turned out that he happened to be one of the men that she would not see again.”
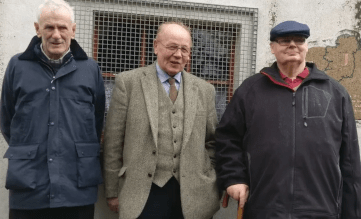
The BBC has recently spoken to three of the IRA men involved the raid.
Micheal Kelly, now in his 80s, has never given an interview before about his role in the attack. “The objective was to attack the barracks, take their guns from them and if necessary, if we had the time and space, to actually destroy the barracks,” he says.
Phil O’Donoghue is also part of the IRA unit. Today, he is honorary president of the 32 County Sovereignty Movement, which is believed to be closely aligned to the Real IRA. He insists the Brookeborough operation was about taking arms rather than killing police officers. “We had strict orders – under no circumstances were we to take on the B Specials (Ulster Special Constabulary) or RUC. We were, if at all possible, to try and take their weapons but we were not in any way to attack them.”
The IRA men arrive in Brookeborough in a stolen tipper lorry, but the driver is unfamiliar with the village and stops in the wrong place. Paddy O’Regan, from Dublin, is in the back of the lorry. His job is to assist Seán South in operating a Bren light machine gun. “When the truck actually stopped, and I got up off the floor and looked over the side of the truck I was looking into a shop – no sign of a barracks.” It is the first in a series of errors – the bomb placed by the station door fails to explode.
Barry Flynn, who has written a history of the border campaign, says he saw Brookeborough as a kind of tragic fiasco. “It became like the Keystone Cops,” he says. “There were a number of grenades thrown at the police station when they found it. One bounced back underneath the lorry and actually damaged the lorry very badly.”
RUC Sgt. Kenneth Cordner is quick to react to the attack. The truck is eventually parked up close to the barracks, allowing Sgt. Cordner a clear field of fire from an upstairs window. Using a Sten sub-machine gun, he opens up with deadly effect on the IRA men below.
Paddy O’Regan is wounded in the ensuing firefight. “We started to return fire on the barracks,” he says. “And after a while I looked down and I saw Seán South lying flat on his face and I felt two thumps in my hip. I knew I was wounded but it didn’t hurt particularly bad. It’s just like somebody hit you a couple of digs and it was just my hips started going numb.”
The order is given to withdraw, according to ex-IRA man Micheal Kelly. “Fergal, the last thing I heard him say, ‘Oh, my legs, oh, my legs!’ He was shot in the legs and bled to death. Seán South, I would say, was dead at this stage.”
The attackers flee across the border leaving the two dead men at a remote farm building where they are found by police.
Bobbie Hanvey is a well-known broadcaster and photographer. In 1957 he is just twelve years old and living across the road from the Brookeborough barracks. He remembers hiding under a bed with two of his friends as the attack unfolded. “The bedroom lit up – it was like daylight with the flames coming out of the guns. That image and the sounds of those guns and that experience has stayed with me to the present day – I’ll never forget it.”
Historian Barry Flynn explains that the Brookeborough raid is also a symbolic moment for the republican movement. The lives of the dead IRA men are subsequently remembered in two famous ballads, “Seán South from Garryowen” and the “Patriot Game.”
“People were writing the songs and, regardless of what was going to happen in the rest of the campaign, the names of Seán South and Fergal O’Hanlon were there forever as the martyrs of Brookeborough”, says Flynn.
The border campaign never again reaches the intensity of the Brookeborough incident, but police officers and IRA men continue to die. The IRA calls a ceasefire in 1962. By then it is clear that its strategy for overthrowing the Stormont government has failed.
(From: “Brookeborough: Failed IRA attack and republican legend” by Robin Sheeran and Bernadette Allen, BBC News NI, http://www.bbc.com, February 22, 2019 | Pictured: Ex-IRA men Micheal Kelly, Phil O’Donoghue and Paddy O’Regan who have a role in the Brookeborough raid)



