On December 12, 1993, a unit of the Provisional Irish Republican Army‘s (IRA) East Tyrone Brigade ambushes a two-men unmarked mobile patrol of the Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC) in Fivemiletown, County Tyrone. Two constables, Andrew Beacom and Ernest Smith, are shot and killed instantly. A military helicopter is also fired at by a second IRA unit in the aftermath of the incident, during a follow-up operation launched in the surroundings of the town by both the British Army and the RUC. A number of suspects are questioned, but the perpetrators make good their escape. The action occurs just three days before the Downing Street Declaration.
Fivemiletown lays in the western edge of the Clogher Valley, near the border between County Fermanagh and County Tyrone. No deaths directly related with paramilitary activity has occurred there during the Troubles prior to the 1993 IRA shootings, though there are a number of incidents in the region in the previous months.
On May 7, 1992, members of the IRA South Fermanagh Brigade detonate a 1,000-pound bomb delivered by a tractor after crossing through a hedge outside the local RUC part-time barracks. The huge explosion leaves ten civilians wounded and causes widespread damage to the surrounding property. The security base itself is heavily damaged and the blast is heard 30 miles away. According to a later IRA statement, the destruction of the security base compels the British forces to organise their patrols from the nearby RUC barracks at Clogher, allowing the East Tyrone Brigade to study their pattern and carry out the 1993 ambush at Fivemiletown’s main street.
A secondary incident occurs some hours later, on May 9, when a British soldier kills his company’s sergeant major in a blue-on-blue shooting at the same place while taking part in a security detail around the wrecked facilities.
On January 20, 1993, the RUC base in Clogher is hit and severely damaged by a Mark-15 “barrack buster” mortar bomb launched by the IRA’s East Tyrone Brigade. A number of constables receive minor injuries.
Constable Andrew Beacom and Reserve Constable Ernest Smith are patrolling Fivemiletown’s Main Street in a civilian-type, unmarked Renault 21 on the early hours of December 12, 1993. Both men are part of the RUC Operational Support Unit, which surveils the border along with the British Army. The constables are based at Clogher RUC barracks.
The IRA reports that two active service units from the East Tyrone Brigade had taken up positions in the centre of Fivemiletown and identified the RUC unmarked vehicle before the ambush.
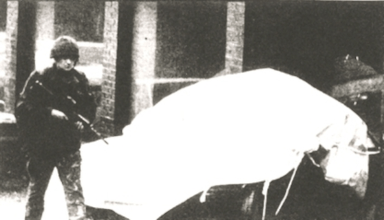
At 1:30 a.m., up to the junction of Main Street and Coneen Street, at least two IRA volunteers open fire from both sides of the road with automatic weapons, hitting the vehicle with more than 20 rounds. Beacom and Smith die on the spot. Constable Beacom lives in Fivemiletown, just a hundred metres from the site of the ambush, where his wife owns a restaurant. She is one of the first persons to arrive to the scene of the shooting. Smith resides with his family at Augher.
According to a colleague in the Operational Support Unit, himself a reserve constable deployed at Lisnaskea and a former Ulster Defence Regiment (UDR) soldier, their deaths “hit the unit very hard.” The men are appreciated for their in-depth knowledge of the area.
A “major” follow-up security operation is mounted between Fivemiletown and the border with the Republic of Ireland, supported by airborne troops and RUC reinforcements, in an attempt to block the attacker’s escape.
Approximately an hour after the ambush, an Army Air Corps (AAC) Westland Lynx helicopter comes upon a number of IRA volunteers in the searching area, just a few miles from the site of the shooting, but the aircraft becomes the target of automatic rifle fire and is forced to disengage. Though the helicopter is not hit, the assailants break contact successfully. The IRA East Tyrone Brigade report claims that the attack on the Westland Lynx is carried out by a second active service unit, which set up a firing position on the predicted path of the British helicopters carrying reinforcements into Fivemiletown after the initial shooting. A number of people are arrested and questioned about the killings, but the perpetrators manage to slip away.
The shootings are widely condemned. RUC Chief Constable Sir Hugh Annesley says that “At a time when the whole community is looking toward peace, the Provisional IRA has yet again shown they have absolutely nothing to offer but deaths and suffering.”
Presbyterian Moderator Rev. Andrew Rodgers calls on the governments to break any contact with Sinn Féin and other “men of blood in both sections of the community.”
A former IRA member cites instead the answer of an IRA volunteer in the area when questioned by him about the futility of the actions at Fivemiletown. He replies that “The war must go on.”
On December 15, 1993, just three days after the attack, the ambush and killing of the two constables at Fivemiletown is mentioned by Member of Parliament Ken Maginnis and Prime Minister John Major during the latter’s speech to the House of Commons right after the joint Downing Street Declaration with Albert Reynolds, the Irish Taoiseach, that sets the basis of the Northern Ireland peace process.
(Pictured: A photograph showing a British Army sentry guarding the scene of the IRA ambush on a Royal Ulster Constabulary mobile patrol, December 12, 1993)

