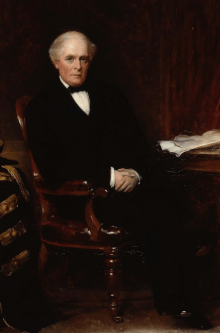
Sir Dominic John Corrigan, 1st Baronet, an Irish physician known for his original observations in heart disease, dies in Dublin on February 1, 1880, following a stroke. The abnormal “collapsing” pulse of aortic valve insufficiency is named Corrigan’s pulse after him.
Corrigan is born in Thomas Street, Dublin, on December 2, 1802, the son of a dealer in agricultural tools. He is educated in St. Patrick’s College, Maynooth, which then has a department for secular students apart from the ecclesiastical seminary. He is attracted to the study of medicine by the physician in attendance and spends several years as an apprentice to the local doctor, Edward Talbot O’Kelly. He studies medicine in Dublin later transferring to Edinburgh Medical School where he receives his degree as MD in August 1825.
Corrigan returns to Dublin in 1825 and sets up a private practice at 11 Ormond Street. As his practice grows, he moves to 12 Bachelors Walk in 1832, and in 1837 to 4 Merrion Square West. Apart from his private practice, he holds many public appointments; he is a physician to St. Patrick’s College, Maynooth, the Sick Poor Institute, the Charitable Infirmary Jervis Street (1830–43) and the House of Industry Hospitals (1840–66). His work with many of Dublin’s poorest inhabitants leads to him specialising in diseases of the heart and lungs, and he lectures and publishes extensively on the subject. He is known as a very hard-working physician, especially during the Great Famine. At the 1870 Dublin City by-election he is elected a Liberal Member of Parliament for Dublin City. In parliament he actively campaigns for reforms to education in Ireland and the early release of Fenian prisoners. He does not stand for re-election in 1874. His support for temperance and Sunday closing of pubs apparently antagonises his constituents and alcohol companies.
In 1847, Corrigan is appointed physician-in-ordinary to the Queen in Ireland. Two years later he is given an honorary MD from Trinity College Dublin (TCD). In 1846 his application to become a fellow of the Royal College of Physicians of Ireland (RCPI) is blocked. In 1855 he gets around this opposition by sitting the college’s entrance exam with the newly qualified doctors. He becomes a fellow in 1856, and in 1859 is elected president, the first Catholic to hold the position. He is re-elected president an unprecedented four times. There is a statue of him in the Graves’ Hall of the college by John Henry Foley.
Corrigan is President of the Royal Zoological Society of Dublin, the Dublin Pathological Society, and the Dublin Pharmaceutical Society. From the 1840s he is a member of the senate of the Queen’s University and in 1871 becomes its vice-chancellor. In 1866 he is created a baronet, of Cappagh and Inniscorrig in the County of Dublin and of Merrion Square in the City of Dublin, partly as a reward for his services as Commissioner of Education for many years. He is a member of the board of Glasnevin Cemetery and a member of the Daniel O’Connell Memorial Committee. Armand Trousseau, the French clinician, proposes that aortic heart disease should be called Corrigan’s disease.
Corrigan marries Joanna Woodlock, the daughter of a wealthy merchant, and sister of the Bishop Dr. Bartholomew Woodlock, in 1827. They have six children, three girls and three boys. His eldest son, Captain John Joseph Corrigan, Dragoon Guards, dies on January 6, 1866, and is interred at the Melbourne General Cemetery, Melbourne, Australia.
Corrigan dies at Merrion Square, Dublin, on February 1, 1880, having suffered a stroke the previous December. He is buried in the crypt of St. Andrew’s Church, Westland Row, Dublin. His grandson succeeds him to the baronetcy.
The Corrigan Ward, a cardiology ward in Beaumont Hospital, Dublin, is named in his honour. Part of his family crest is also part of the Beaumont Hospital crest.