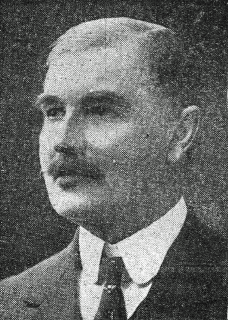
Alan Bell, policeman and resident magistrate, is tasked by British Intelligence to track down Michael Collins’s war chest. By March 26, 1920, he has successfully confiscated over £71,000 from Sinn Féin‘s headquarters and by investigating banks throughout the country and is set to seize much more. On that day he is pulled off a tram in South Dublin and shot three times in the head.
Bell is born in Banagher, King’s County (now County Offaly), one of at least two sons of the Rev. James Adamson Bell, Church of Ireland clergyman. His mother’s name is unknown. Educated locally, he joins the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) in September 1879 as a cadet, serving in the counties of Cavan, Galway, Roscommon, Westmeath, and Cork up to the rank of district inspector. During the Land War (1879–82) he investigates sources of Irish National Land League funds and in 1882 arrests the American land reformer and journalist Henry George in Athenry. He, along with District Inspector William Henry Joyce, compile evidence against the nationalist and agrarian agitation for the special commission of 1888–89 which investigates charges against the nationalist leader Charles Stewart Parnell and his associates. His actions make him popular with unionists but a marked man among nationalists.
After almost twenty years’ police service, Bell becomes a resident magistrate on November 12, 1898, a civil service post under the Constabulary Act, 1836. His districts included Athenry, Claremorris, Armagh, Belfast, and Portadown. With many years’ experience in criminal intelligence, he is transferred to Dublin Castle early in the Irish War of Independence as a special investigator and intelligence gatherer. In December 1919 he questions suspects for the attempted Irish Republican Army (IRA) assassination of the viceroy, Lord French, and place suspect premises under surveillance. His vulnerability is made evident by the shooting in January 1920 of Dublin Metropolitan Police assistant commissioner William C. Redmond, one of his informants. He remains in Dublin to investigate the “republican loan” raised by Michael Collins and Sinn Féin, believed to be hidden in suspect bank accounts. Refusing protective accommodation in Dublin Castle where other officials have already retreated, he opts to live with his wife at a private suburban residence, 19 Belgrave Square, Monkstown, County Dublin. He summons bank managers to his office in early March 1920 and progresses sufficiently to force Collins into taking action.
Carrying a pocket revolver for protection, Bell travels to work daily by tram until the morning of March 26, 1920. At the busy junction of Simmonscourt Road, Sandymount Avenue, and Merrion Road, Ballsbridge, a group of men immobilise the crowded vehicle and surround their target, declaring, “Come on, Mr. Bell, your time has come.” Bundling him on to the street, they shoot him dead in public view and run from the scene. In spite of vivid eyewitness accounts in the press, no killer is identified. His death comes amid almost daily violence and barely a week after the shooting of the Sinn Féin Lord Mayor of Cork, Tomás Mac Curtain, allegedly by police assassins. He acts fearlessly, perhaps expecting a violent death as the outcome of his mission.
Bell is buried privately in Dean’s Grange Cemetery, Deansgrange, County Dublin. Some Irish republican prisoners at Gloucester during the influenza epidemic of 1918–19 may have been saved from infection by his brother, who as prison doctor there had advised that the jail be evacuated.
(From: “Alan Bell” by Patrick Long, Dictionary of Irish Biography, http://www.dib.ie, October 2009)

