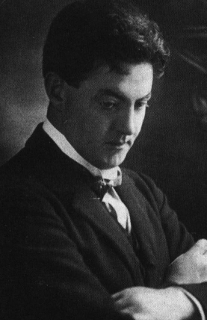Michele Esposito, Italian composer, conductor and pianist who spends most of his professional life in Dublin, dies on November 19, 1929.
Esposito is born at Castellammare di Stabia, near Naples, Italy, on September 29, 1855. In 1865, he wins a scholarship to the Naples Conservatory as a piano pupil of Beniamino Cesi, himself a favourite pupil of Sigismond Thalberg, and studies composition there for eight years under Paolo Serrao, teacher of Francesco Cilea and others. He is a near-contemporary of Giuseppe Martucci, and a few years the senior of Alessandro Longo, both taught by these teachers. In 1878, he goes to Paris for several years where he establishes a growing reputation.
In 1879, Esposito marries Natalia Klebnikoff, the only daughter of Pierre Klebnikoff, professor of chemistry and physics at Saint Petersburg University. They have four children, including the noted scholar, Mario Esposito.
On December 24, 1881, Esposito is visited by an old friend, Caracciolo, who is principal professor of singing at the Royal Irish Academy of Music (RIAM) in Dublin. Upon his recommendation, Esposito is offered the position of chief pianoforte professor of piano at the RIAM at Easter 1882.
Esposito remains in Dublin for more than forty years, devoting himself to the encouragement of classical music in Dublin. He inaugurates the Royal Dublin Society (RDS) chamber music recitals, with great success, and gives piano recitals for the Society every year. He establishes the Dublin Orchestral Society in 1898 and is its conductor until its disbandment in 1914. He is also the conductor of the Sunday Orchestral Concerts until they are discontinued in 1914. He conducts concerts of the London Symphony Orchestra at Woodbrook in 1913 and 1914, and also performs his piano concerto with them under the baton of Hamilton Harty. Together with Sir Stanley Cochrane, he founds the music publishing company C. E. Edition.
Esposito receives awards from the Feis Ceoil for his cantata Deirdre, his Irish Symphony and his String Quartet in D major. His Cello Sonata wins a prize from the London Incorporated Society of Musicians in 1899. His Violin Sonata in E minor gains a prize offered by La Société Nouvelle, Paris, in 1907, and his String Quartet in C minor wins another offered by the Accademia Filarmonica di Bologna.
In 1923, King Victor Emmanuel III awards Esposito the Order of the Crown of Italy, with the title “Commendatore,” to mark his contribution to Irish music.
Esposito retires in 1928 and returns to Italy after failing to revive the Dublin Orchestral Society the previous year. He dies on November 19, 1929, in Florence. He is buried at the Cimitero di Trespiano where his gravestone is inscribed with three bars of music by “H. H.” Of his four children, Vera Esposito is involved in Irish theatre, and Mario Esposito becomes a scholar of Latin learning in medieval Ireland.