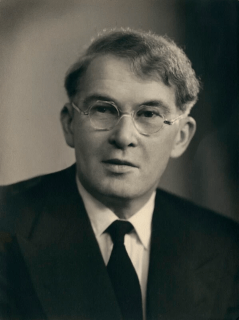
Brendan Bracken, Irish-born businessman, politician and a Minister of Information and First Lord of the Admiralty in Winston Churchill‘s War Cabinet, is born on February 15, 1901, in Church Street, Templemore, County Tipperary.
Bracken is the third child and second of three sons of Joseph Kevin (J. K.) Bracken and Hannah Bracken (née Ryan). The family moves to Kilmallock, County Limerick, in 1903, the year before his father’s death. By 1908, his mother takes the family to live in Glasnevin, a new suburb in north Dublin, and subsequently off the North Circular Road. He is educated in St. Patrick’s National School, Drumcondra, and at the Christian Brothers‘ O’Connell School in North Richmond Street. He is a mischievous, delinquent child, one time throwing a schoolfellow into the Royal Canal. In February 1915 he is sent to Mungret College, a Jesuit boarding school near Limerick. He is not amenable to the regime and runs away on several occasions, finding accommodation in local hotels under a false name.
At the end of 1915 Bracken goes to Australia with £14 in his pocket. He is first based in Echuca, Victoria, where he is put up in a convent. Later he moves to other houses run by religious orders. A voracious reader, he claims that he is doing research for a life of Cardinal Patrick Francis Moran, and signs himself “Brendan Newman Bracken.” He seeks admission as a pupil to Riverview, the fashionable Jesuit school in Sydney, claiming that he had been educated at Clongowes Wood College. Unfortunately for him, a priest who had just come out from Clongowes exposes him. Opinionated and argumentative, he does not conceal his skepticism about the Catholic religion. For a time, he teaches in a Protestant school in Orange, New South Wales.
Bracken returns to Ireland in 1919. By this time his mother has remarried and is living with her new husband, Patrick Laffan, on a farm in Beauparc, County Meath. After a short stay there, he moves to Liverpool and finds employment as a teacher at the Liverpool Collegiate School, claiming that he had been to the University of Sydney. He teaches at the school for two terms in 1920, earning extra money as tutor to a young boy. With his savings he is able to gain admission to Sedbergh School, a public school in the town of Sedbergh in Cumbria, North West England, giving his name as Brendan Rendall Bracken, born 1904, and stating that his parents had perished in a bush fire in Australia, leaving him money to complete his education. He remains only one term but distinguishes himself by winning a prize for history. After Sedbergh, Bracken teaches at Rottingdean preparatory school and then at Bishops Stortford School. He cuts a flamboyant figure and drops the name of famous acquaintances with gay abandon. He stands over 6 feet and has a powerful presence and a domineering personality; his mop of red hair and pale freckled skin combine with black teeth to give him a bizarre appearance.
In 1922 Bracken moves to London. He takes charge of the Illustrated Review when its editor, Hilaire Belloc, resigns. Renamed English Life and covering political and social events, it affords Bracken an opportunity to meet prominent people, including J. L. Garvin, editor of The Observer. In autumn 1923 Garvin introduces him to Winston Churchill, who had lost his parliamentary seat in 1922 and decided to contact Leicester West in the 1923 United Kingdom general election. Bracken offers his services as campaign manager. The friendship between Churchill and Bracken is soon so close that Bracken is rumoured to be Churchill’s natural son. Churchill’s wife Clementine dislikes Bracken and discourages the friendship.
Meanwhile Bracken enjoys the life of a ubiquitous socialite and builds up his career in publishing. He becomes a director of Eyre & Spottiswoode in 1926, starting The Banker, a monthly magazine, for them, and acquiring the Financial News in 1928 and a half-share in The Economist. To these are added in due course the Investors Chronicle and The Practitioner. His success in business enables him to acquire a home in North Street in 1928, near the Houses of Parliament. He is driven about in a chauffeured Hispano-Suiza car.
In 1929, Bracken has himself adopted as conservative candidate for Paddington North, a marginal seat. After a hard-fought campaign characterised by minor violence provoked by Bracken’s intemperate language, he wins the seat by 528 votes. At one point a rumour is put about that Bracken is in reality a Polish Jew, which he has to disprove by exhibiting a copy of his birth certificate. His background is a subject of speculation among acquaintances, and in throwaway remarks he gives different fictitious versions of it, Ireland figuring in none of them. He does however remain in constant touch with his mother, to whom he seems to have been deeply devoted, until her death in 1928. However, he has as little contact as possible with his brother and sisters, although he does give assistance to some of them and their families at various times.
In parliament Bracken voices right-wing views on economic issues and is an enthusiastic imperialist. After Churchill resigns from the conservative front bench in 1930 because they would not oppose the Labour government’s proposal for Indian self-government, he is supported by Bracken. During the 1930s, when Churchill is in the wilderness, disagreeing with the party leadership on India and on what he sees as a policy of appeasement toward Hitler‘s Germany, Bracken is his sole political ally. Stanley Baldwin calls him Churchill’s “faithful chela.”
In September 1939, Churchill joins Neville Chamberlain‘s war cabinet as First Lord of the Admiralty. Bracken is appointed his parliamentary private secretary, continuing in that role when Churchill becomes Prime Minister. Despite the king’s opposition, Churchill insists in June 1940 that Bracken should be appointed a privy councillor. Bracken shuts up his house and moves to the Prime Minister’s residence for the duration of the war. As a confidant of the Prime Minister, he often acts as a go-between with other politicians and newspapermen. He is allowed to oversee patronage and takes a special interest in ecclesiastical appointments. In July 1941, he is persuaded by Lord Beaverbrook and Churchill to become Minister for Information. He wins over most of the proprietors by giving them more news, often on a confidential basis, and censorship is kept to a minimum. The BBC is also allowed a fair measure of freedom as long as it behaves responsibly; under the leadership of Cyril Radcliffe, the civil service head of the ministry, it operates more smoothly. Bracken was generally acclaimed for that success.
After the resignation of the Labour ministers from the government at the end of the war in Europe, Bracken joins the cabinet as First Lord of the Admiralty. He is prominent in the general election campaign that follows and is the only conservative minister apart from Churchill to give more than one radio broadcast. He is accused, probably unjustly, of provoking Churchill to take extreme positions, and blamed when the conservatives are heavily defeated at the polls. Bracken himself loses Paddington North to Lt. Gen. Sir Noel Mason-MacFarlane. However, he is soon back in parliament representing Bournemouth, and as front-bench spokesman is an uncompromising opponent of the nationalisation measures of the Labour government (1945–51). He is out of sympathy with the leftward drift of the conservative party associated with Rab Butler and Harold Macmillan.
In December 1951, when Churchill is again Prime Minister, Bracken declines an invitation to serve as Colonial Secretary, pleading that his recurring sinusitis makes it impossible. He resigns his seat in the House of Commons and is created a peer, Viscount Bracken of Christchurch in Hampshire, but never takes his seat in the House of Lords. Although he retires from politics, he remains close to political events through his friendship with Churchill. He is deeply involved in concealing the severe stroke that Churchill suffers in 1953, so that he can carry on as Prime Minister.
In the postwar period, Bracken has important business interests. The Financial News group acquires the Financial Times in 1945, and he is returned as chairman of the expanded company. He writes a weekly Financial Times column until 1954. He oversees the building near St. Paul’s of a new head office, named “Bracken House” after his death. He is also chairman of the Union Corporation mining house, with interests in South Africa, which he frequently visits. From 1950 he is chairman of the board of governors of Sedbergh School, where he goes frequently and often walks for miles across the fells. He organises and finances the restoration of the eighteenth-century school building as a library, with a commemoratory inscription, “Remember Winston Churchill.”
From 1955 Bracken is a trustee of the National Gallery. He is an unrelenting opponent of the proposal to return to Ireland the impressionist paintings bequeathed to it by Hugh Lane, because a codicil willing them to Dublin has not been witnessed. Throughout the postwar period he carries on a prolific correspondence with friends such as Lord Beaverbrook, the American ambassador Lewis Douglas, and the Australian entrepreneur W. S. Robinson. These are a valuable and entertaining source on the political history of the time.
In January 1958, Bracken, who has always been a heavy smoker, is diagnosed with throat cancer. He lingers on until August 8, 1958, when he dies at the flat of his friend Sir Patrick Hennessy in Park Lane. He resists efforts made to reconcile him to the church of Rome. By his own wish he is cremated, and his ashes are scattered on Romney Marsh, Kent. On his instructions his papers are burned by his chauffeur. His estate comes to £145,032.
(From: “Bracken, Brendan” by Charles Lysaght, Dictionary of Irish Biography, www. dib.ie, October 2009 | Pictured: Brendan Bracken, bromide print by Elliott & Fry, January 13, 1950, National Portrait Gallery, London)


