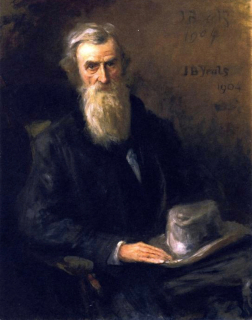
John O’Leary, Irish republican and a leading Fenian, is born on July 23, 1830, in Tipperary, County Tipperary. He is imprisoned in England during the nineteenth century for his involvement in the Irish Republican Brotherhood.
O’Leary, born a Catholic, is educated at the local Protestant grammar school, The Abbey School, and later the Catholic Carlow College. He identifies with the views advocated by Thomas Davis and meets James Stephens in 1846.
He begins his studies in law at Trinity College, Dublin, in 1847, where, through the Grattan Club, he associates with Charles Gavan Duffy, James Fintan Lalor and Thomas Francis Meagher.
After the failure of the Young Ireland Rebellion of 1848, O’Leary attempts to rescue the Young Ireland leaders from Clonmel Gaol, and is himself imprisoned for a week from September 8, 1849. He takes part in a further attempted uprising in Cashel on September 16, 1849, but this proves abortive.
O’Leary abandons his study of law at Trinity College because he is unwilling to take the oath of allegiance required of a barrister. He enrolls at Queen’s College, Cork in 1850, to study medicine, later moving to Queen’s College, Galway, then on to further studies at Meath Hospital in Dublin, in Paris and in London. In 1855, he visits Paris, where he becomes acquainted with Kevin Izod O’Doherty, John Martin and the American painter, James Abbott McNeill Whistler. He subsequently becomes financial manager of the newly formed Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) and is joint editor of the IRB paper The Irish People.
On September 16, 1865, O’Leary is arrested and later tried on charges of high treason, eventually reduced to “treason felony.” He is sentenced to twenty years of penal servitude, of which five years are spent in English prisons, prior to his release and exile in January 1871. During his exile, he lives mainly in Paris, also visiting the United States, remains active in the IRB and its associated organisations, and writes many letters to newspapers and journals.
On the expiration of his 20-year prison term and therefore of the conditions associated with his release in 1885, O’Leary returns to Ireland. He and his sister, the poet Ellen O’Leary, both become important figures within Dublin cultural and nationalist circles, which include William Butler Yeats, Maud Gonne, Rose Kavanagh, Rosa Mulholland, George Sigerson, and Katharine Tynan. He also functions as an elder statesman of the separatist movement, being active in the Young Ireland Society, and acts as president of the Irish Transvaal Committee, which supports the Boer side in the Second Boer War.
John O’Leary dies at his residence in Dublin on the evening of March 16, 1907. He is referred to famously by W.B. Yeats in his poem September 1913: “Romantic Ireland’s dead and gone/It’s with O’Leary in the grave.”
(Pictured: Painting of John O’Leary, a favorite subject of John Butler Yeats (1904). The National Gallery of Ireland owns three oil portraits of O’Leary.)





 On February 8, 1923, the
On February 8, 1923, the 


