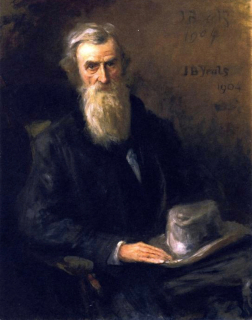Helena Mary Molony, prominent Irish republican, feminist and labour activist, dies in Dublin on January 28, 1967. She fights in the 1916 Easter Rising and later becomes the second woman president of the Irish Trades Union Congress (ITUC).
Molony is born in Dublin on January 15, 1883, to Michael Molony, a grocer, and Catherine McGrath. Her mother dies early in her life. Her father later remarries, but both became alcoholics, something which influences her years later.
In 1903, inspired by a pro-nationalist speech given by Maud Gonne, Molony joins Inghinidhe na hÉireann and begins a lifelong commitment to the nationalist cause. In 1908 she becomes the editor of the organisation’s monthly newspaper, Bean na hÉireann (Woman of Ireland). The newspaper brings together a nationalist group – Constance Markievicz designs the title page and writes the gardening column, Sydney Gifford writes for the paper and is on its production team and contributors include Eva Gore-Booth, Susan L. Mitchell, and Katharine Tynan, as well as Patrick Pearse, Thomas MacDonagh, George William Russell, Roger Casement, Arthur Griffith and James Stephens.
Molony is central to the school meals activism of the movement. With Maud Gonne, Marie Perolz and others, she organises the supply of daily school meals to children in impoverished areas, and pressures Dublin Corporation and other bodies to provide proper meals to the starved children of Dublin city.
Molony also has a career as an actress and is a member of the Abbey Theatre. However, her primary commitment is to her political work. She is a strong political influence, credited with bringing many into the movement, including Constance Markievicz and Dr. Kathleen Lynn.
As a labour activist, Molony is a close colleague of Markievicz and of James Connolly. In November 1915 Connolly appoints her secretary of the Irish Women Workers’ Union, in succession to Delia Larkin. This union had been formed during the strike at Jacob’s Biscuit Factory that was part of the 1913 Dublin lock-out. She manages the union’s shirt factory in Liberty Hall, founded to give employment to the strikers put out of work and blacklisted after the strike. She is friendly with the family of Thomas MacDonagh and his wife, Muriel, and is the godmother of their daughter Barbara, whose godfather is Patrick Pearse.
Fianna Éireann, the cadet body of the Irish Volunteers, is founded by Constance Markievicz in Molony’s home at 34 Lower Camden Street, Dublin, on August 16, 1909. Markievicz works closely with Molony and Bulmer Hobson in organising the fledgling Fianna. It is during this period of working together in building the Fianna that Molony and Hobson grow close and became romantically linked. However, the relationship does not last.
Molony is a prominent member of Cumann na mBan, the republican women’s paramilitary organisation formed in April 1914 as an auxiliary of the Irish Volunteers. Members of Cumann na mBan train alongside the men of the Irish Volunteers in preparation for the armed rebellion against the English forces in Ireland.
During the 1916 Easter Rising, Molony is one of the Citizen Army soldiers who attacks Dublin Castle. During the defence of City Hall, her commanding officer, Sean Connolly, is killed and she is captured and imprisoned until December 1916.
After the Irish Civil War, Molony becomes the second female president of the Irish Trades Union Congress. She remains active in the republican cause during the 1930s, particularly with the Women’s Prisoner’s Defense League and the People’s Rights Association.
Molony retires from public life in 1946 but continued to work for women’s labour rights. She dies in Dublin on January 28, 1967.