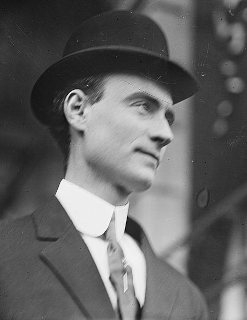William Owen “Buckey” O’Neill, a sheriff, newspaper editor, miner, politician, Georgist, gambler and lawyer, mainly in Arizona, is born the first of four children to John Owen, an Irish immigrant, and Mary O’Neill (nee McMenimin) in St. Louis, Missouri, on February 2, 1860.
O’Neill’s father most likely arrived in the United States during the 1850s. By Spring 1862, the family has moved to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. When the American Civil War begins, his father joins the 116th Pennsylvania Volunteers. On December 13, 1862, during the Battle of Fredericksburg, he is wounded and serves the rest of the war as a member of the Invalid Corps. The younger O’Neill is educated at Gonzaga College High School and Georgetown Law School.
During the first part of 1879, O’Neill responds to an item in The Washington Star calling for men to migrate to the Arizona Territory. He arrives in Phoenix, riding a burro, in September of the same year. Upon his arrival in town, he is hired as a printer by the Phoenix Herald. By late 1880, he has become bored with the position and seeks to experience the “Real West” in the boomtown of Tombstone, Arizona.
In Tombstone, O’Neill takes the opportunity to experience the local saloons before taking a job with The Tombstone Epitaph. By mid-1881 he again feels a wanderlust and leaves town. Where he goes next is unknown, one story having him journey to Hawaii, unlikely due to the travel time, and then traveling through California. He is known to visit Santa Fe before going to Albuquerque, New Mexico and works briefly as a court reporter. In early 1882, he is back in Phoenix working as a deputy to Marshal Henry Garfias. Several weeks later he moves to Prescott, his home for the next fifteen years.
In Prescott O’Neill rapidly progresses in his journalistic career. Starting as a court reporter, he soon founds his own newspaper, Hoof and Horn, a paper for the livestock industry. He becomes the editor of the Arizona Miner weekly newspaper in 1884 to February 1885.
In 1886, O’Neill becomes captain of the Prescott Grays, the local unit of the Arizona Militia. On February 5, 1886, Dennis Dilda, a convicted murderer, is hanged. O’Neill and the Prescott Grays stand honor guard for the event. When the trap drops, O’Neill faints, which causes him severe embarrassment. He later writes a story called “The Horse of the Hash-Knife Brand.” In it, a member of a posse admits to nearly fainting at the hanging of a horse thief.
On April 27, 1886, O’Neill marries Pauline Schindler. They have a son, but he dies shortly after being born premature.
In 1888, while serving as Yavapai County, Arizona judge, O’Neill is elected county sheriff, running on the Republican ticket.
On March 20, 1889, four masked men, William Sterin, John Halford, Daniel Harvick, and J. J. Smith, rob the Atlantic and Pacific Railroad passenger train in Canyon Diablo. A four-man posse, made up of O’Neill, Jim Black, Carl Holton, and Ed St. Clair, is soon formed and they take off after the robbers. On April 1, the posse catches up with the robbers. After exchanging rifle shots, the posse captures the four men. During the fight, no men are injured, but one of the robber’s horses is killed. All four are sent to the Yuma Territorial Prison but are pardoned eight years later. There is unfounded speculation that, in 1898, Sterin enlists under a false name in the Rough Riders and is killed in action in the Battle of San Juan Hill.
After his term is up, O’Neill is unanimously elected mayor of Prescott. In 1894 and 1896 he runs for Delegate to the United States House of Representatives from Arizona Territory, running on the People’s Party ticket.
In 1897, after years of speculating on mines, O’Neill sells a group of claims near the Grand Canyon to Chicago backers, who also propose building a railroad from Williams to the mines and the South Rim. He becomes a director of the development companies, and soon begins railroad surveys, mine developments, and building a smelter. He also uses profits to begin building rental buildings, leading him to financial independence.
O’Neill also helps introduce a bill allowing women to vote in municipal elections in 1897. Although he convinces his Populist friends to sign the bill into law, the high court dismisses the bill in 1899.
In 1898, war breaks out between the United States and Spain. O’Neill joins Theodore Roosevelt‘s Rough Riders and becomes Captain of Troop A. First Lieutenant Frank Frantz serves as O’Neil’s Deputy Commander. Along with Alexander Brodie and James McClintock, he tries to make an entire regiment made up of Arizona cowboys. Eventually though, only three troops are authorized.
The Rough Riders land at Daiquirí on June 22, 1898. Two Buffalo Soldiers of the 10th Cavalry Regiment fall overboard. Upon seeing this, O’Neill jumps into the water in full uniform and sabre. He searches for the men for two minutes before having to come up for breath.
On June 25, 1898, the Rough Riders see their first action. O’Neill leads his men at the front of the line in the Battle of Las Guasimas, capturing the Spanish flank. During the action he sees several men, who he believes to be Spaniards, across the road from him, and shouts “Hostiles on our right, fire at will!” He learns after the firing ceases that the men he exchanged shots with were Cuban rebels.
On July 1, 1898, at about 10:00 a.m., the Rough Riders and the 10th Cavalry are stationed below Kettle Hill. The Spaniards, who are on top of the hill, pour Mauser rifle fire down on the Americans. O’Neill is killed in action.
Before the fighting is over, O’Neill’s men bury him on the slope of San Juan Hill. After the war, his family and friends enlist help from the United States Department of War to find and recover his body. After six men fail to find the site, the War Department sends Henry Alfred Brown, the Rough Riders’ Chaplain, to find him. Despite it being eight months since O’Neill’s death, Chaplain Brown locates the site within two hours after arriving in Santiago de Cuba. The well-preserved body is exhumed, placed in a coffin, and returned to the United States on the Army transport Crook. He is buried at Arlington National Cemetery, in Arlington County, Virginia. The epitaph on his gravestone reads, “Who would not die for a new star on the flag?”
On July 3, 1907, a monument by sculptor Solon Borglum is dedicated to O’Neill and the other Rough Riders in their memory in Prescott, Arizona. Seven thousand people gather to witness the unveiling.
O’Neill Spring, in the Pumphouse Wash wetlands south of Flagstaff, Arizona, is named after O’Neill, as is O’Neill Butte in the Grand Canyon and Bucky O’Neill Hill in Bisbee, Arizona. Bucky (sic) O’Neill is a main character in the TNT movie Rough Riders, portrayed by Sam Elliott.