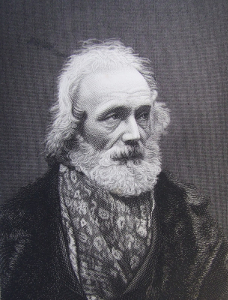James Stephens, Irish novelist and poet, is born in Dublin on February 9, 1880.
Stephens’ mother works in the home of the Collins family of Dublin and is adopted by them. He is committed to the Meath Protestant Industrial School for Boys as a small child and spends his childhood there. He attends school with his adopted brothers Thomas and Richard before graduating as a solicitor’s clerk. He is known affectionately in school as “Tiny Tim” due to his 4’10” stature. He is much enthralled by the tales of military valour of his adoptive family and would have become a soldier if not for his height.
By the early 1900s Stephens is increasingly inclined to socialism and the Irish language and by 1912 is a dedicated Irish Republican. He is a close friend of the 1916 Easter Rising leader Thomas MacDonagh, who is then editor of The Irish Review and deputy headmaster in St. Enda’s School, the radical bilingual school run by Patrick Pearse. His growing nationalism brings a schism with his adopted family, but probably wins him his job as registrar in the National Gallery of Ireland, where he works between 1915 and 1925, having previously had an ill-paid job with the Mecredy solicitors’ firm.
Stephens produces many retellings of Irish myths and fairy tales. His retellings are marked by a rare combination of humour and lyricism. He also writes several original novels, The Crock of Gold, Etched in Moonlight and Demi-Gods, based loosely on Irish fairy tales. The Crock of Gold in particular has achieved enduring popularity and has often been reprinted.
Stephens begins his career as a poet under the tutelage of “Æ” (George William Russell). His first book of poems, Insurrections, is published in 1909. His last book, Kings and the Moon (1938), is also a volume of verse.
Stephens’s influential account of the 1916 Easter Rising, Insurrection in Dublin, describes the effect of the deaths by execution of his friend Thomas MacDonagh and others as being “like watching blood oozing from under a door.” Of MacDonagh he writes:
No person living is the worse off for having known Thomas MacDonagh, and I, at least, have never heard MacDonagh speak unkindly or even harshly of anything that lived. It has been said of him that his lyrics were epical; in a measure it is true, and it is true in the same measure that his death was epical. He was the first of the leaders who was tried and shot.
Stephens lives between Paris, London and Dublin. During the 1930s he is a friend of James Joyce, and they mistakenly believe that they share a birthday. Joyce, who is concerned about his ability to finish what later becomes Finnegans Wake, proposes that Stephens assist him, with the authorship credited to JJ & S, short “Jameses Joyce & Stephens,” but also a pun on the popular Irish whiskey made by John Jameson & Sons. The plan is never implemented, as Joyce is able to complete the work on his own.
During the last decade of Stephens’ life, he finds a new audience through a series of broadcasts on the BBC. He dies at Eversleigh on Saint Stephen’s Day, December 26, 1950.