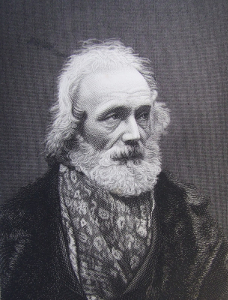
James Henry, Irish classical scholar and poet, is born in Dublin on December 13, 1798.
Henry is the son of a woolen draper, Robert Henry, and his wife Kathleen Elder. He is educated by Unitarian schoolmasters and then at Trinity College, Dublin. At age 11 he falls in love with the poetry of Virgil and gets into the habit of always carrying a copy of the Aeneid in his left breast-pocket.
Henry graduates from Trinity with the gold medal for Classics. He then turns to medicine and practises as a physician in Dublin until 1845. In spite of his unconventionality and unorthodox views on religion and his own profession, he is very successful. He marries Anne Jane Patton, from Donegal, and has three daughters, only one of whom, Katherine, born in 1830, survives infancy.
His accession to a large fortune in 1845 enables him to devote himself entirely to the absorbing occupation of his life – the study of Virgil. Accompanied by his wife and daughter, he visits all those parts of Europe where he is likely to find rare editions or manuscripts of the poet. When his wife dies in Tyrol he continues his work with his daughter, who becomes quite a Virgil expert in her own right, and crosses the Alps seventeen times. After the death of his daughter in 1872 he returns to Dublin and continues his research at Trinity College, Dublin.
As a commentator on Virgil, Henry will always deserve to be remembered, notwithstanding the occasional eccentricity of his notes and remarks. The first fruits of his researches are published at Dresden in 1853 under the quaint title Notes of a Twelve Years Voyage of Discovery in the first six Books of the Eneis. These are embodied, with alterations and additions, in the Aeneidea, or Critical, Exegetical and Aesthetical Remarks on the Aeneis (1873-1892), of which only the notes on the first book are published during Henry’s lifetime. As a textual critic Henry is exceedingly conservative. His notes, written in a racy and interesting style, are especially valuable for their wealth of illustration and references to the less-known classical authors.
Henry is also the author of five collections of verse plus two long narrative poems describing his travels, and various pamphlets of a satirical nature. At its best his poetry has something of the flavour of Robert Browning and Arthur Hugh Clough while at its worst it resembles the doggerel of William McGonagall. His five volumes of verse are all published at his own expense and receive no critical attention either during or after his lifetime.
James Henry dies at Dalkey, County Dublin, on July 14, 1876.




 The
The