John Jeffreys Pratt, 1st Marquess Camden, a British politician, is born at Lincoln’s Inn Fields, London, on February 11, 1759. He is styled Viscount Bayham from 1786 to 1794 and known as the 2nd Earl Camden from 1794 to 1812. He serves as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland in the revolutionary years 1795 to 1798 and as Secretary of State for War and the Colonies between 1804 and 1805.
Pratt is born the only son of the barrister Charles Pratt, 1st Earl Camden, and Elizabeth, daughter of Nicholas Jeffreys, of The Priory, Brecknockshire, Wales. He is baptised on the day Halley’s Comet appears. In 1765, his father is created Baron Camden, at which point he becomes The Hon. John Pratt. He is educated at the University of Cambridge (Trinity College).
In 1780, Pratt is elected Member of Parliament for Bath and obtains the position of Teller of the Exchequer the same year, a lucrative office which he keeps until his death, although after 1812 he refuses to receive the large income arising from it. He serves under William Perry, 2nd Earl of Shelburne, as Lord of the Admiralty between 1782 and 1783 and in the same post under William Pitt the Younger between 1783 and 1789, as well as a Lord of the Treasury between 1789 and 1792.
In 1786, Pratt’s father is created Earl Camden, at which point he becomes known by one of his father’s subsidiary titles as Viscount Bayham.
In 1793, Pratt is sworn of the Privy Council. In 1794 he succeeds his father as 2nd Earl Camden, and the following year he is appointed Lord Lieutenant of Ireland by Pitt.
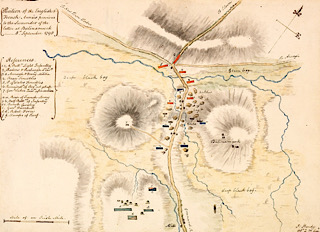
As an opponent of parliamentary reform and of Catholic emancipation, Pratt’s term of office is one of turbulence, culminating in the Irish Rebellion of 1798. His refusal in 1797 to reprieve the United Irishman William Orr, convicted of treason on the word of one witness of dubious credit (and for which his own sister, Frances Stewart, Marchioness of Londonderry, petitions him), arouses great public indignation. To break the United Irish conspiracy, he suspends habeas corpus and unleashes a ruthless martial law campaign to disarm and break up the republican organization.
Pratt resigns from office in June 1798, to be replaced with Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis, who oversees the military defeat of the rebellion. In 1804, Pratt becomes Secretary of State for War and the Colonies under Pitt, and in 1805 Lord President of the Council, an office he retains until 1806. He is again Lord President from 1807 to 1812, after which date he remains for some time in the cabinet without office. In 1812 he is created Earl of Brecknock and Marquess Camden.
The enforced resignation from the Cabinet of Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh, the stepson of his sister Frances (Lady Londonderry), to whom he has always been personally close, in September 1809, leads to a series of bitter family quarrels, when it becomes clear that Pratt has known for months of the plan to dismiss Stewart, but has given him no warning. Stewart himself regards Pratt as “a weak friend,” not an enemy, and they are eventually reconciled. Other members of the Stewart family, however, never forgive Pratt for what they regard as his disloyalty.
Pratt is also Lord Lieutenant of Kent between 1808 and 1840 and appoints himself Colonel of the Cranbrook and Woodsgate Regiment of Local Militia in 1809. He is Chancellor of the University of Cambridge between 1834 and 1840. He is made a Knight of the Garter in 1799 and elected a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London in 1802.
Pratt marries Frances, daughter of William Molesworth, in 1785. She dies at Bayham Abbey, Sussex, in July 1829. He survives her by eleven years and dies at Seal, Kent, on October 8, 1840, aged 81. He is succeeded by his only son, George.
The family owns and lives in a house located at 22 Arlington Street in St. James’s, a district of the City of Westminster in central London, which adjoins The Ritz Hotel. In the year of his death, he sells the house to Henry Somerset, 7th Duke of Beaufort.