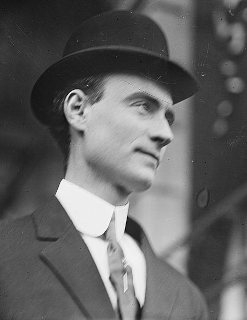Papal Count John Francis McCormack, KSG, KSS, KHS, Irish tenor celebrated for his performances of the operatic and popular song repertoires, and renowned for his diction and breath control, dies in Booterstown, Dublin, on September 16, 1945.
McCormack is born on June 14, 1884, in Athlone, County Westmeath, the second son and fifth of the 11 children of Andrew McCormack and his wife Hannah Watson. His parents are both from Galashiels, Scotland, and work at the Athlone Woolen Mills, where his father is a foreman. He is baptised in St. Mary’s Church, Athlone, on June 23, 1884.
McCormack receives his early education from the Marist Brothers in Athlone and later attends Summerhill College, Sligo. He sings in the choir of the old St. Peter’s Church in Athlone under his choirmaster Michael Kilkelly. When the family moves to Dublin, he sings in the choir of St. Mary’s Pro-Cathedral where he is discovered by Vincent O’Brien. In 1903 he wins the coveted gold medal of the Dublin Feis Ceoil. He marries Lily Foley in 1906 and they have two children, Cyril and Gwen.
In March 1904, McCormack becomes associated with James Joyce, who at the time has singing ambitions himself. He persuades Joyce to enter the Feis Ceoil that year, where the not yet famous writer is awarded the Bronze Medal.
Fundraising activities on his behalf enable McCormack to travel to Italy in 1905 to receive voice training by Vincenzo Sabatini, father of the novelist Rafael Sabatini, in Milan. Sabatini finds McCormack’s voice naturally tuned and concentrates on perfecting his breath control, an element that becomes part of the basis of his renown as a vocalist.
In 1906, McCormack makes his operatic début at the Teatro Chiabrera, Savona. The next year, he begins his first important operatic performance at Covent Garden in Pietro Mascagni‘s Cavalleria rusticana, becoming the theatre’s youngest principal tenor. In 1909, he begins his career in the United States.
In February 1911, McCormack plays Lieutenant Paul Merrill in the world premiere of Victor Herbert‘s opera Natoma with Mary Garden in the title role. Later that year, he tours Australia after Dame Nellie Melba engages him, then at the height of his operatic career, aged 27, as a star tenor for the Melba Grand Opera Season. He returns for concert tours in subsequent years.
By 1912, McCormack is beginning to become involved increasingly with concert performances, where his voice quality and charisma ensures that he becomes the most celebrated lyric tenor of his time. He does not, however, retire from the operatic stage until after his performance of 1923 in Monte Carlo, although by then the top notes of his voice have contracted. Famous for his extraordinary breath control, he can sing 64 notes on one breath in Mozart‘s “Il mio tesoro” from Don Giovanni, and his Handelian singing is just as impressive in this regard.
McCormack makes hundreds of recordings, his best-known and most commercially successful series of records being those for the Victor Talking Machine Company during the 1910s and 1920s. He is Victor’s most popular Red Seal recording artist after tenor Enrico Caruso. In the 1920s, he sings regularly on radio and later appears in two sound films, Song o’ My Heart (1930), playing an Irish tenor, and as himself appearing in a party scene in Wings of the Morning (1937), the first British three-strip Technicolor feature.
McCormack is one of the first artists to record the popular ballad “I Hear You Calling Me” written in 1908 by Harold Harford and Charles Marshall. He records it twice for Odeon Records starting in 1908 and a further four times for Victor between 1910 and 1927, becoming his best seller. He is the first artist to record the famous World War I song “It’s a Long Way to Tipperary” in 1914. He also records a best-selling version of another popular World War I tune, “Keep the Home Fires Burning,” in 1917. He also sings songs expressive of Irish nationalism and endorses the Irish Nationalist estrangement from the United Kingdom. He is associated particularly with the songs of Thomas Moore, notably “The Harp That Once Through Tara’s Halls,” “The Minstrel Boy,” “Believe Me If All (Those Endearing Young Charms),” and “The Last Rose of Summer.” Between 1914 and 1922, he records almost two dozen songs with violin accompaniment provided by Fritz Kreisler, with whom he also tours. He records songs of Hugo Wolf for the Hugo Wolf Society in German. In 1918, he records the song “Calling Me Home to You.”
In 1917, McCormack becomes a naturalised citizen of the United States. In June 1918, he donates $11,458 toward the U.S. World War I effort. By then, his career is a huge financial success, earning millions in his lifetime from record sales and appearances.
By 1920, Edwin Schneider has become McCormack’s accompanist and the two are “inseparable.” When Schneider retires, Gerald Moore takes over as accompanist from 1939 to 1943.
In 1927, McCormack moves into Moore Abbey, Monasterevin, County Kildare, and adopts a very opulent lifestyle by Irish standards. He also owns apartments in London and New York. He hopes that one of his racehorses, such as Golden Lullaby, would win The Derby, but this never occurs.
McCormack also purchases Runyon Canyon in Hollywood in 1930 from Carman Runyon. He sees and likes the estate while there filming Song o’ My Heart (1930), an early all-talking, all-singing picture. He uses his salary for this movie to purchase the estate and builds a mansion he calls ‘San Patrizio,’ after Saint Patrick. He and his wife live in the mansion until they return to England in 1938.
McCormack tours often, and in his absence, the mansion is often let to celebrities such as Janet Gaynor and Charles Boyer. The McCormacks make many friends in Hollywood, among them Errol Flynn, Will Rogers, John Barrymore, Basil Rathbone, Ronald Colman, Charles E. Toberman and the Dohenys. After his farewell tour of America in 1937, the McCormacks deed the estate back to Carman Runyon expecting to return to the estate at a later date. World War II intervenes and he does not return.
McCormack originally ends his career at the Royal Albert Hall in London, during 1938. However, one year after that farewell concert, he is back singing for the Red Cross and in support of the war effort. He gives concerts, tours, broadcasts and records in this capacity until 1943 when poor health finally forces him to retire permanently.
Ill with emphysema, McCormack purchases a house near the sea, “Glena,” Booterstown, Dublin. After years of increasingly poor health, and a series of infectious illnesses, including influenza and pneumonia, he dies at his home in Booterstown on September 16, 1945. He is buried in Deans Grange Cemetery, St. Patrick’s section, plot reference E/120.