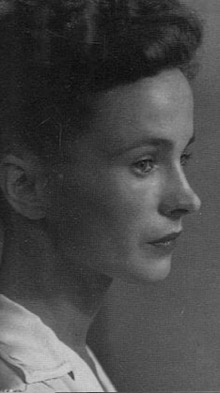Agnes Winifred O’Farrelly (Irish: Úna Ní Fhaircheallaigh), academic and Professor of Irish at University College Dublin (UCD), dies in Dublin on November 5, 1951.
O’Farrelly is born Agnes Farrelly on June 24, 1874, in Raffony House, Virginia, County Cavan, one of five daughters and three sons of Peter Dominic Farrelly and Ann Farrelly (née Sheridan), a family with a traditional interest in the Irish language. After her articles Glimpses of Breffni and Meath are published in The Anglo-Celt in 1895, the editor, E. T. O’Hanlon, encourages her to study literature. Graduating from the Royal University of Ireland (BA 1899, MA 1900), she is appointed a lecturer in Irish at Alexandra College and Loreto College. A founder member in 1902, along with Mary Hayden, of the Irish Association of Women Graduates and Candidate Graduates, to promote equal opportunity in university education, she gives evidence to the Robertson (1902) and Fry (1906) commissions on Irish university education, arguing successfully for full co-education at UCD. Appointed lecturer in modern Irish at UCD in 1909, she is also a member of the first UCD governing body and the National University of Ireland (NUI) senate (1914–49). In 1932, on the retirement of Douglas Hyde, she is appointed professor of modern Irish at UCD, holding the position until her retirement in 1947. She is also president of the Irish Federation of University Women (1937–39) and of the National University Women Graduates’ Association (NUWGA) (1943–47).
One of the most prominent women in the Gaelic League, a member of its coiste gnótha (executive committee) and a director of the Gaelic press An Cló-Chumann Ltd, O’Farrelly is a close friend of most of its leading figures, especially Douglas Hyde, Kuno Meyer, and Eoin MacNeill. One of Hyde’s allies in his battle to avoid politicising the league, she is so close to him that students at UCD enjoy speculating about the nature of their friendship. She advocates pan-Celticism, but does not get involved in disputes on the matter within the league. A founder member, and subsequently principal for many years, of the Ulster College of Irish, Cloghaneely, County Donegal, she is also associated with the Leinster and Connacht colleges and serves as chairperson of the Federation of Irish Language Summer Schools.
Having presided at the inaugural meeting of Cumann na mBan in 1914, espousing its subordinate role in relation to the Irish Volunteers, O’Farrelly leaves the organisation soon afterward because of her support for recruitment to the British Army during World War I. A close friend of Roger Casement, in 1916, along with Col. Maurice Moore she gathers a petition that seeks a reprieve of his death sentence. She is a member of a committee of women which negotiate unsuccessfully with Irish Republican Army (IRA) leaders to avoid civil war in 1922, and is heavily defeated as an independent candidate for the NUI constituency in the general elections of 1923 and June 1927. In 1937 she is actively involved in the National University Women Graduates’ Association’s campaign against the constitution, seeking deletion of articles perceived as discriminating against women.
Popular among students at UCD, O’Farrelly has a reputation as a social figure and entertains frequently at her homes in Dublin and the Donegal Gaeltacht. A founder member (1914) and president (1914–51) of the UCD camogie club, she persuades William Gibson, 2nd Baron Ashbourne, to donate the Ashbourne Cup for the camogie intervarsities. She is also president of the Camogie Association of Ireland in 1941–42. A supporter of native Irish industry, she is president of the Irish Industrial Development Association and the Homespun Society, and administrator of the John Connor Magee Trust for the development of Gaeltacht industry. A poet and writer in both Irish and English, often using the pseudonym ‘Uan Uladh’, her principal publications in prose are The reign of humbug (1900), Leabhar an Athar Eoghan (1903), Filidheacht Segháin Uí Neachtáin (1911), and her novel Grádh agus crádh (1901); and in poetry Out of the depths (1921) and Áille an domhain (1927).
O’Farrelly retires from UCD in 1947, and lives at 38 Brighton Road, Rathgar. An oil portrait by Seán Keating, RHA, is presented to her by the NUWGA on her retirement. She dies on November 5, 1951 in Dublin. Taoiseach Éamon de Valera and President Seán T. O’Kelly attend her funeral to Dean’s Grange Cemetery. She never marries, and leaves an estate valued at £3,109.