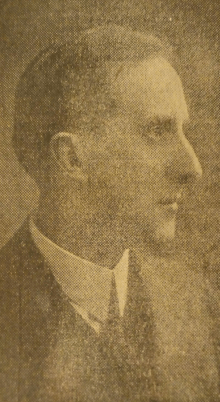John Kelly, Northern Irish republican politician, is born in the New Lodge area of Belfast, Northern Ireland, on April 5, 1936. He joins the Irish Republican Army (IRA) in the 1950s and is a founder member and a leader of the Provisional Irish Republican Army in the early 1970s.
Kelly is one of five sons and four daughters born to William Kelly, retail and wholesale fruitier, and his wife Margaret (née Maginness). Living off Carlisle Circus in a flashpoint area of north Belfast and close to Crumlin Road Gaol, the Kellys are a strongly republican family, regularly supplying republican inmates with fruit and assisting them on their release.
Later in life Kelly moves to Maghera, County Londonderry, where he lives until his death in 2007. He and his wife have a daughter. He is a dedicated member of local Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) club Watty Graham’s GAC, Glen and a keen supporter of Gaelic games and the Irish language.
Kelly joins the IRA in the early 1950s when he is eighteen and takes part in the Border Campaign of 1956–62 but is arrested in December 1956 and imprisoned until 1963. He is a member of the Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association (NICRA) in 1967–69 which leads on to sectarian riots in Belfast. A leader of the newly formed Provisional IRA in 1969, he is involved in the formation of “citizens’ defence groups” to protect nationalist areas of Belfast from loyalist rioters who are largely unhampered by the police.
Kelly is jailed on three occasions for IRA related activity spending a total of fifteen years in prison in Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. His first term is for his activity in the 1956 IRA border campaign. He also serves a six-month term in 1973 in the Republic of Ireland for being a member of the IRA.
Commenting later on the Troubles, Kelly says, “Yes, it was a terrible period. But you can’t turn the clock back. The Irish government did not create the Provisional IRA. What happened was as inevitable as the changing seasons.”
The citizens’ defence groups seek help from the government in Dublin in 1969, then led by Jack Lynch. Several ministers respond and arrange a fund of £100,000 but the planned arms shipment fails. Kelly later says, “These discussions were all about guns. The whole thing was government-sponsored, government-backed and government-related.” The planning includes travel to Britain, Europe, and on to the United States where he meets the founders of NORAID. He is one of the co-defendants in the subsequent Dublin “Arms Trial” with ministers Charles Haughey and Neil Blaney, accused of conspiring to import arms illegally into the Republic of Ireland. The trial eventually collapses from a lack of evidence, as the relevant government files are kept secret, but the Irish government sacks several ministers as a result.
Kelly goes into electoral politics, serving on Magherafelt District Council from 1997. At the 1998 Northern Ireland Assembly election he is elected to the Northern Ireland Assembly as a Sinn Féin member for Mid Ulster. He is deselected before the 2003 election, and criticises the decision by the Sinn Féin leadership to support policing reforms. In January 2006 he co-writes a letter with Brendan Hughes which casts doubt on the claims that dissident republicans have threatened Sinn Féin leaders and claims that the real threats are being made by the Sinn Féin leadership against those who seek a debate on policing. He leaves Sinn Féin which he considers too controlled from the centre, opposing the leadership “deceit and the philosophy of creative ambiguity,” and he retires from politics.
Kelly dies in Maghera following a long battle with cancer on September 5, 2007. Many tributes are paid to him including a minute’s silence before the Derry Senior Football Championship quarter final between St. Patrick’s GAC, Loup, and Dungiven GAC on September 8, 2007, at the home of his local club, Watty Graham GAC, Glen. A Na Piarsaigh Belfast GAC jersey is draped over his coffin before he is interred at Maghera Catholic Graveyard.