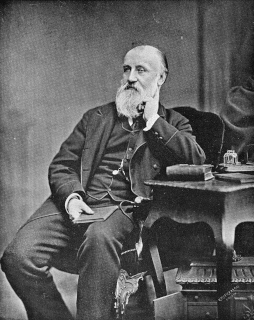Estella Frances Solomons, one of the leading Irish artists of her generation, is born into a prominent Jewish family in Dublin on April 2, 1882. She is noted for her portraits of contemporaries in the republican movement and her studio is a safe house during the Irish War of Independence.
Solomons is born to Maurice Solomons and poet Rosa Jane Jacobs. Her father is an optician whose practice in 19 Nassau Street, Dublin, is mentioned in Ulysses. Her father is also the Vice-Consul of Austria-Hungary. The Solomons family, who came to Dublin from England in 1824, are one of the oldest continuous lines of Jews in Ireland.
Solomons grandmother, Rosa Jacobs Solomons, who is born in Hull in England, is the author of a book called Facts and Fancies (Dublin 1883). Her brother, Bethel Solomons, a renowned physician, a master of the Rotunda Hospital and Irish international rugby player, is mentioned in Finnegans Wake. Her brother Edwin is a stockbroker and prominent member of the Dublin Jewish community. Her younger sister Sophie is a trained opera singer. A portrait of Sophie, by her cousin the printmaker Louise Jacobs, survives in the Estella Solomons archives in the Library of Trinity College Dublin (TCD).
In 1898, at the age of 16, Solomons enters the Dublin Metropolitan School of Art where she wins a significant prize. Her classmates include future Irish artists including Mary Swanzy, Eva Hamilton and William J. Leech. She also attends the Chelsea School of Art from 1903 to 1906. A visit to the tercentenary exhibition of the work of Rembrandt in Amsterdam in 1903 impacts her creative practice and possibly influences her adoption of printmaking as her principal vehicle of expression. She studies under two of Ireland’s leading artists, Walter Osborne, who is another major influence, and William Orpen. With her friends Cissie Beckett (aunt of Samuel Beckett) and Beatrice Elvery, she goes to study in Paris at Académie Colarossi. On her return she exhibits in Leinster Hall, Molesworth Street, with contemporaries such as Beatrice Elvery, Eva Hamilton and Grace Gifford. Her work is also included in joint exhibitions with other artists at Mills Hall and the Arlington Gallery, London. She also exhibits at her Great Brunswick Street studio in December 1926.
Solomons illustrates Padraic Colum‘s The Road Round Ireland (1926) and DL Kelleher’s The Glamour of Dublin in 1928. Originally published after the devastation of the 1916 Easter Rising, the later edition features eight views of familiar locations in the city centre including Merchant’s Arch and King’s Inns. Her etching “A Georgian Doorway” is included in Katherine MacCormack’s Leabhar Ultuin in 1920. This publication features illustrations by several prominent Irish artists and is sold in aid of the new Saint Ultan’s Children’s Hospital in Charlemont Street, Dublin, that had been founded by two prominent members of Cumann na mBan, Dr. Kathleen Lynn and Madeleine ffrench-Mullen.
Solomons paints landscapes and portraits, including of artist Jack Yeats, politician Arthur Griffith, poet Austin Clarke, and writers James Stephens and George Russell (Æ).
Solomons is elected an associate of the Royal Hibernian Academy (RHA) in July 1925, but it is not until 1966 that she is elected an honorary member. Her work is included in the Academy’s annual members’ exhibition every year for sixty years.
Solomons is married to poet and publisher Seumas O’Sullivan, whose birth name is James Sullivan Starkey. Her parents oppose the relationship as O’Sullivan is not of the Jewish faith. They marry in 1925, when she is 43 and he 46, after her parents have died. She collaborates with her husband on The Dublin Magazine (1923–58), the renowned literary and art journal, of which O’Sullivan is editor for 35 years. She provides vital financial support to the magazine, particularly in sourcing advertising, which is difficult in the tough economic climate of the new Free State. She is helped in this endeavour by poet and writer, Kathleen Goodfellow, a lifelong friend. When Solomons and O’Sullivan are looking to move from their house in Rathfarnham because of a damp problem, Goodfellow offers them the house beside her own on Morehampton Road for a nominal rent. Two of Solomons’ portraits of Goodfellow are in the Model Arts and Niland Gallery in Sligo.
Solomons joins the Ranelagh branch of Cumann na mBan at the same time as Goodfellow. They are taught first aid, drilling and signaling by Phyllis Ryan. She is active before and during the Irish War of Independence. She conceals ammunition in the family vegetable garden before delivering it to a Sinn Féin agent. Her studio at Great Brunswick Street is used as a safe house by republican volunteers. During this time, she paints the portraits of a number of revolutionaries, some of which she has to later destroy to avoid incriminating them. Her work includes a portrait of Frank Aiken when we was chief of staff of the Irish Republican Army (IRA).
Solomons takes up a teaching position at Bolton Street College, Dublin. In 1939, she organises an exhibition in Dublin to help refugee artists from Europe.
Solomons dies on November 2, 1968, and is buried in Woodtown Cemetery, Rathfarnham. Her friend Kathleen Goodfellow gifts the Morehampton Road Wildlife Sanctuary, where Solomons liked to paint, to An Taisce. Two plaques have subsequently been erected there, one in memory of Solomons and one for Goodfellow.
Some of Solomons works are held in the Niland Collection, at The Model gallery in Sligo and in the National Gallery of Ireland. Her archives, which include artwork and photographs (and prints by Louise Jacobs), and the archives of The Dublin Magazine are in the Library of Trinity College Dublin.